1 为什么使用关联
在 Rails 中,关联在两个 Active Record 模型之间建立联系。模型之间为什么要有关联?因为关联能让常规操作变得更简单。例如,在一个简单的 Rails 应用中,有一个作者模型和一个图书模型。每位作者可以著有多本图书。不用关联的话,模型可以像下面这样定义:
class Author < ApplicationRecord end class Book < ApplicationRecord end
现在,假如我们想为一位现有作者添加一本书,得这么做:
@book = Book.create(published_at: Time.now, author_id: @author.id)
假如要删除一位作者的话,也要把属于他的书都删除:
@books = Book.where(author_id: @author.id) @books.each do |book| book.destroy end @author.destroy
使用 Active Record 关联,Rails 知道两个模型之间有联系,上述操作(以及其他操作)可以得到简化。下面使用关联重新定义作者和图书模型:
class Author < ApplicationRecord has_many :books, dependent: :destroy end class Book < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :author end
这么修改之后,为某位作者添加新书就简单了:
@book = @author.books.create(published_at: Time.now)
删除作者及其所有图书也更容易:
@author.destroy
请阅读下一节,进一步学习不同的关联类型。后面还会介绍一些使用关联时的小技巧,然后列出关联添加的所有方法和选项。
2 关联的类型
Rails 支持六种关联:
-
belongs_to -
has_one -
has_many -
has_many :through -
has_one :through -
has_and_belongs_to_many
关联使用宏式调用实现,用声明的形式为模型添加功能。例如,声明一个模型属于(belongs_to)另一个模型后,Rails 会维护两个模型之间的“主键-外键”关系,而且还会向模型中添加很多实用的方法。
在下面几小节中,你会学到如何声明并使用这些关联。首先来看一下各种关联适用的场景。
2.1 belongs_to 关联
belongs_to 关联创建两个模型之间一对一的关系,声明所在的模型实例属于另一个模型的实例。例如,如果应用中有作者和图书两个模型,而且每本书只能指定给一位作者,就要这么声明图书模型:
class Book < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :author end
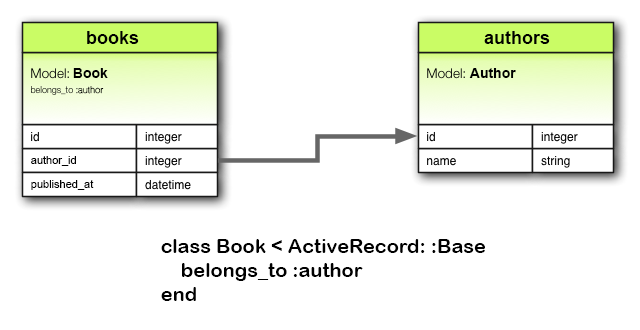
在 belongs_to 关联声明中必须使用单数形式。如果在上面的代码中使用复数形式定义 author 关联,应用会报错,提示“uninitialized constant Book::Authors”。这是因为 Rails 自动使用关联名推导类名。如果关联名错误地使用复数,推导出的类名也就变成了复数。
相应的迁移如下:
class CreateBooks < ActiveRecord::Migration[5.0]
def change
create_table :authors do |t|
t.string :name
t.timestamps
end
create_table :books do |t|
t.belongs_to :author, index: true
t.datetime :published_at
t.timestamps
end
end
end
2.2 has_one 关联
has_one 关联也建立两个模型之间的一对一关系,但语义和结果有点不一样。这种关联表示模型的实例包含或拥有另一个模型的实例。例如,应用中每个供应商只有一个账户,可以这么定义供应商模型:
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord has_one :account end
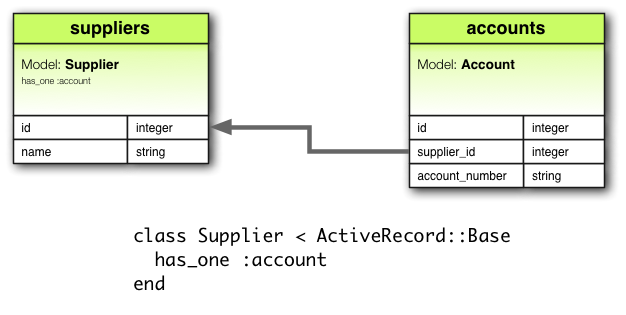
相应的迁移如下:
class CreateSuppliers < ActiveRecord::Migration[5.0]
def change
create_table :suppliers do |t|
t.string :name
t.timestamps
end
create_table :accounts do |t|
t.belongs_to :supplier, index: true
t.string :account_number
t.timestamps
end
end
end
根据使用需要,可能还要为 accounts 表中的 supplier 列创建唯一性索引和(或)外键约束。这里,我们像下面这样定义这一列:
create_table :accounts do |t|
t.belongs_to :supplier, index: { unique: true }, foreign_key: true
# ...
end
2.3 has_many 关联
has_many 关联建立两个模型之间的一对多关系。在 belongs_to 关联的另一端经常会使用这个关联。has_many 关联表示模型的实例有零个或多个另一模型的实例。例如,对应用中的作者和图书模型来说,作者模型可以这样声明:
class Author < ApplicationRecord has_many :books end
声明 has_many 关联时,另一个模型使用复数形式。
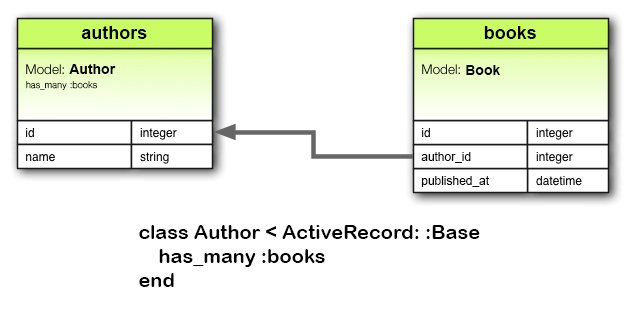
相应的迁移如下:
class CreateAuthors < ActiveRecord::Migration[5.0]
def change
create_table :authors do |t|
t.string :name
t.timestamps
end
create_table :books do |t|
t.belongs_to :author, index: true
t.datetime :published_at
t.timestamps
end
end
end
2.4 has_many :through 关联
has_many :through 关联经常用于建立两个模型之间的多对多关联。这种关联表示一个模型的实例可以借由第三个模型,拥有零个和多个另一模型的实例。例如,在医疗锻炼中,病人要和医生约定练习时间。这中间的关联声明如下:
class Physician < ApplicationRecord has_many :appointments has_many :patients, through: :appointments end class Appointment < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :physician belongs_to :patient end class Patient < ApplicationRecord has_many :appointments has_many :physicians, through: :appointments end
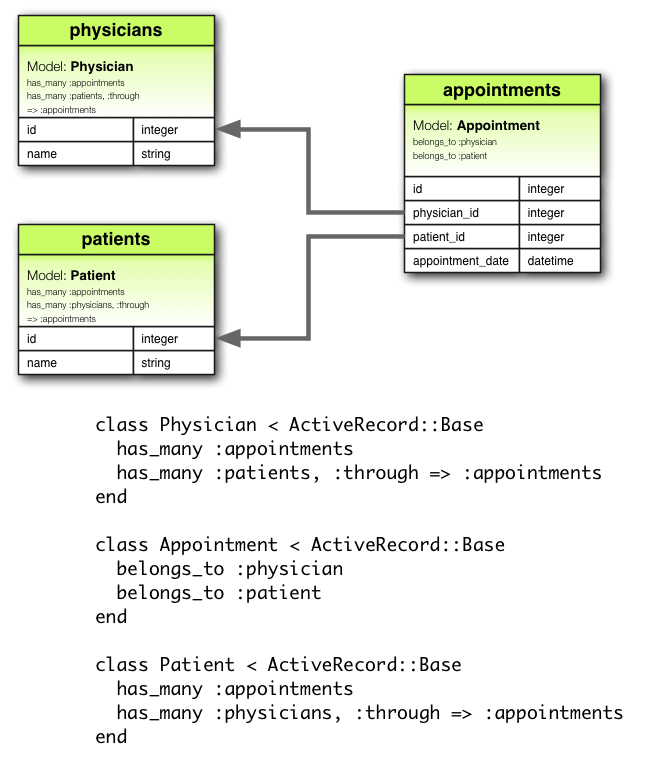
相应的迁移如下:
class CreateAppointments < ActiveRecord::Migration[5.0]
def change
create_table :physicians do |t|
t.string :name
t.timestamps
end
create_table :patients do |t|
t.string :name
t.timestamps
end
create_table :appointments do |t|
t.belongs_to :physician, index: true
t.belongs_to :patient, index: true
t.datetime :appointment_date
t.timestamps
end
end
end
联结模型可以使用 has_many 关联方法管理。例如:
physician.patients = patients
会为新建立的关联对象创建联结模型实例。如果其中一个对象删除了,相应的联结记录也会删除。
自动删除联结模型的操作直接执行,不会触发 *_destroy 回调。
has_many :through 还能简化嵌套的 has_many 关联。例如,一个文档分为多个部分,每一部分又有多个段落,如果想使用简单的方式获取文档中的所有段落,可以这么做:
class Document < ApplicationRecord has_many :sections has_many :paragraphs, through: :sections end class Section < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :document has_many :paragraphs end class Paragraph < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :section end
加上 through: :sections 后,Rails 就能理解这段代码:
@document.paragraphs
2.5 has_one :through 关联
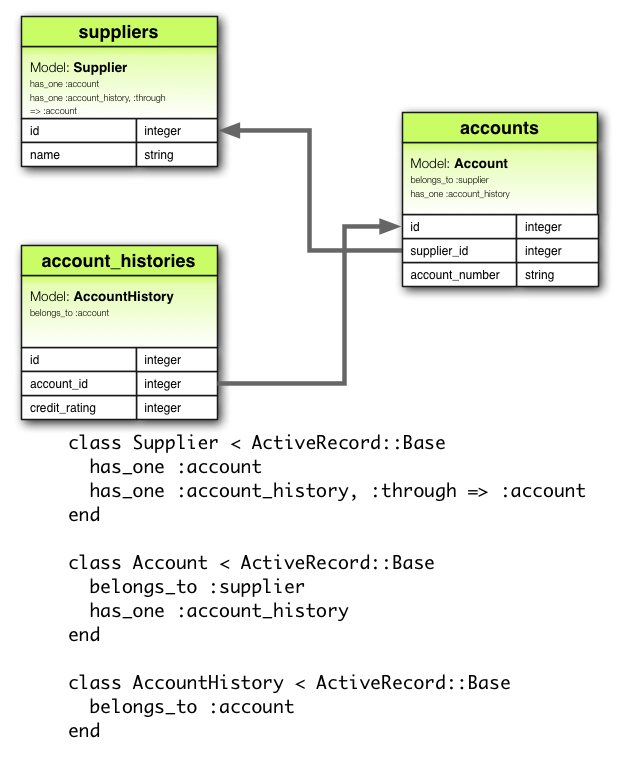
has_one :through 关联建立两个模型之间的一对一关系。这种关联表示一个模型通过第三个模型拥有另一模型的实例。例如,每个供应商只有一个账户,而且每个账户都有一个账户历史,那么可以这么定义模型:
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord has_one :account has_one :account_history, through: :account end class Account < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :supplier has_one :account_history end class AccountHistory < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :account end
相应的迁移如下:
class CreateAccountHistories < ActiveRecord::Migration[5.0]
def change
create_table :suppliers do |t|
t.string :name
t.timestamps
end
create_table :accounts do |t|
t.belongs_to :supplier, index: true
t.string :account_number
t.timestamps
end
create_table :account_histories do |t|
t.belongs_to :account, index: true
t.integer :credit_rating
t.timestamps
end
end
end
2.6 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联
has_and_belongs_to_many 关联直接建立两个模型之间的多对多关系,不借由第三个模型。例如,应用中有装配体和零件两个模型,每个装配体有多个零件,每个零件又可用于多个装配体,这时可以按照下面的方式定义模型:
class Assembly < ApplicationRecord has_and_belongs_to_many :parts end class Part < ApplicationRecord has_and_belongs_to_many :assemblies end
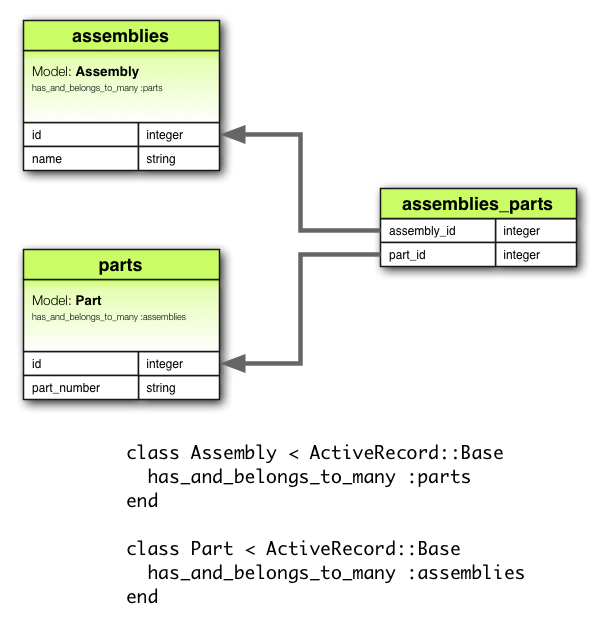
相应的迁移如下:
class CreateAssembliesAndParts < ActiveRecord::Migration[5.0]
def change
create_table :assemblies do |t|
t.string :name
t.timestamps
end
create_table :parts do |t|
t.string :part_number
t.timestamps
end
create_table :assemblies_parts, id: false do |t|
t.belongs_to :assembly, index: true
t.belongs_to :part, index: true
end
end
end
2.7 在 belongs_to 和 has_one 之间选择
如果想建立两个模型之间的一对一关系,要在一个模型中添加 belongs_to,在另一模型中添加 has_one。但是怎么知道在哪个模型中添加哪个呢?
二者之间的区别是在哪里放置外键(外键在 belongs_to 关联所在模型对应的表中),不过也要考虑数据的语义。has_one 的意思是某样东西属于我,即哪个东西指向你。例如,说供应商有一个账户,比账户拥有供应商更合理,所以正确的关联应该这么声明:
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord has_one :account end class Account < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :supplier end
相应的迁移如下:
class CreateSuppliers < ActiveRecord::Migration[5.0]
def change
create_table :suppliers do |t|
t.string :name
t.timestamps
end
create_table :accounts do |t|
t.integer :supplier_id
t.string :account_number
t.timestamps
end
add_index :accounts, :supplier_id
end
end
t.integer :supplier_id 更明确地表明了外键的名称。在目前的 Rails 版本中,可以抽象实现的细节,使用 t.references :supplier 代替。
2.8 在 has_many :through 和 has_and_belongs_to_many 之间选择
Rails 提供了两种建立模型之间多对多关系的方式。其中比较简单的是 has_and_belongs_to_many,可以直接建立关联:
class Assembly < ApplicationRecord has_and_belongs_to_many :parts end class Part < ApplicationRecord has_and_belongs_to_many :assemblies end
第二种方式是使用 has_many :through,通过联结模型间接建立关联:
class Assembly < ApplicationRecord has_many :manifests has_many :parts, through: :manifests end class Manifest < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :assembly belongs_to :part end class Part < ApplicationRecord has_many :manifests has_many :assemblies, through: :manifests end
根据经验,如果想把关联模型当做独立实体使用,要用 has_many :through 关联;如果不需要使用关联模型,建立 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联更简单(不过要记得在数据库中创建联结表)。
如果要对联结模型做数据验证、调用回调,或者使用其他属性,要使用 has_many :through 关联。
2.9 多态关联
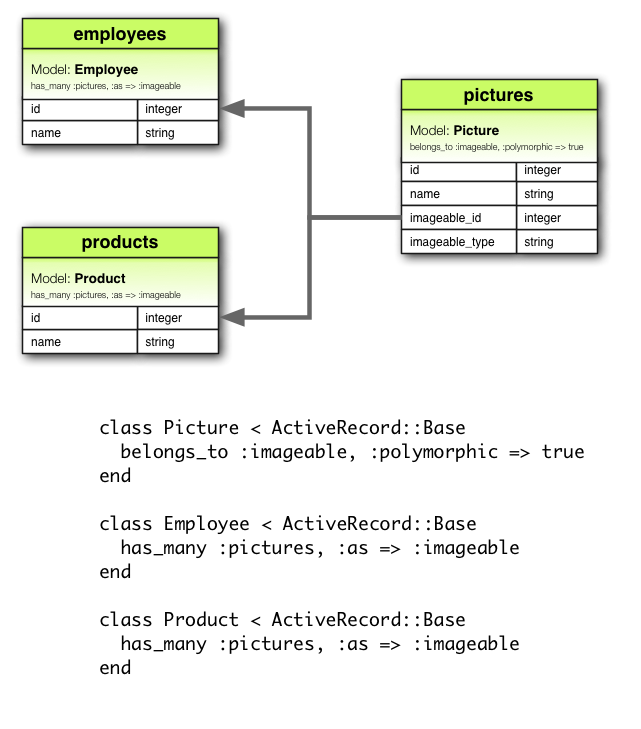
关联还有一种高级形式——多态关联(polymorphic association)。在多态关联中,在同一个关联中,一个模型可以属于多个模型。例如,图片模型可以属于雇员模型或者产品模型,模型的定义如下:
class Picture < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :imageable, polymorphic: true end class Employee < ApplicationRecord has_many :pictures, as: :imageable end class Product < ApplicationRecord has_many :pictures, as: :imageable end
在 belongs_to 中指定使用多态,可以理解成创建了一个接口,可供任何一个模型使用。在 Employee 模型实例上,可以使用 @employee.pictures 获取图片集合。
类似地,可使用 @product.pictures 获取产品的图片。
在 Picture 模型的实例上,可以使用 @picture.imageable 获取父对象。不过事先要在声明多态接口的模型中创建外键字段和类型字段:
class CreatePictures < ActiveRecord::Migration[5.0]
def change
create_table :pictures do |t|
t.string :name
t.integer :imageable_id
t.string :imageable_type
t.timestamps
end
add_index :pictures, [:imageable_type, :imageable_id]
end
end
上面的迁移可以使用 t.references 简化:
class CreatePictures < ActiveRecord::Migration[5.0]
def change
create_table :pictures do |t|
t.string :name
t.references :imageable, polymorphic: true, index: true
t.timestamps
end
end
end
2.10 自联结
设计数据模型时,模型有时要和自己建立关系。例如,在一个数据库表中保存所有雇员的信息,但要建立经理和下属之间的关系。这种情况可以使用自联结关联解决:
class Employee < ApplicationRecord
has_many :subordinates, class_name: "Employee",
foreign_key: "manager_id"
belongs_to :manager, class_name: "Employee"
end
这样定义模型后,可以使用 @employee.subordinates 和 @employee.manager 检索了。
在迁移(模式)中,要添加一个引用字段,指向模型自身:
class CreateEmployees < ActiveRecord::Migration[5.0]
def change
create_table :employees do |t|
t.references :manager, index: true
t.timestamps
end
end
end
3 小技巧和注意事项
为了在 Rails 应用中有效使用 Active Record 关联,要了解以下几点:
- 控制缓存
- 避免命名冲突
- 更新模式
- 控制关联的作用域
- 双向关联
3.1 控制缓存
关联添加的方法都会使用缓存,记录最近一次查询的结果,以备后用。缓存还会在方法之间共享。例如:
author.books # 从数据库中检索图书 author.books.size # 使用缓存的图书副本 author.books.empty? # 使用缓存的图书副本
应用的其他部分可能会修改数据,那么应该怎么重载缓存呢?在关联上调用 reload 即可:
author.books # 从数据库中检索图书
author.books.size # 使用缓存的图书副本
author.books.reload.empty? # 丢掉缓存的图书副本
# 重新从数据库中检索
3.2 避免命名冲突
关联的名称并不能随意使用。因为创建关联时,会向模型添加同名方法,所以关联的名字不能和 ActiveRecord::Base 中的实例方法同名。如果同名,关联方法会覆盖 ActiveRecord::Base 中的实例方法,导致错误。例如,关联的名字不能为 attributes 或 connection。
3.3 更新模式
关联非常有用,但没什么魔法。关联对应的数据库模式需要你自己编写。不同的关联类型,要做的事也不同。对 belongs_to 关联来说,要创建外键;对 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联来说,要创建相应的联结表。
3.3.1 创建 belongs_to 关联所需的外键
声明 belongs_to 关联后,要创建相应的外键。例如,有下面这个模型:
class Book < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :author end
上述关联需要在 books 表中创建相应的外键:
class CreateBooks < ActiveRecord::Migration[5.0]
def change
create_table :books do |t|
t.datetime :published_at
t.string :book_number
t.integer :author_id
end
add_index :books, :author_id
end
end
如果声明关联之前已经定义了模型,则要在迁移中使用 add_column 创建外键。
为了提升查询性能,最好为外键添加索引;为了保证参照完整性,最好为外键添加约束:
class CreateBooks < ActiveRecord::Migration[5.0]
def change
create_table :books do |t|
t.datetime :published_at
t.string :book_number
t.integer :author_id
end
add_index :books, :author_id
add_foreign_key :books, :authors
end
end
3.3.2 创建 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联所需的联结表
创建 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联后,必须手动创建联结表。除非使用 :join_table 选项指定了联结表的名称,否则 Active Record 会按照类名出现在字典中的顺序为表起名。因此,作者和图书模型使用的联结表默认名为“authors_books”,因为在字典中,“a”在“b”前面。
模型名的顺序使用字符串的 <=> 运算符确定。所以,如果两个字符串的长度不同,比较最短长度时,两个字符串是相等的,那么长字符串的排序比短字符串靠前。例如,你可能以为“paper_boxes”和“papers”这两个表生成的联结表名为“papers_paper_boxes”,因为“paper_boxes”比“papers”长,但其实生成的联结表名为“paper_boxes_papers”,因为在一般的编码方式中,“_”比“s”靠前。
不管名称是什么,你都要在迁移中手动创建联结表。例如下面的关联:
class Assembly < ApplicationRecord has_and_belongs_to_many :parts end class Part < ApplicationRecord has_and_belongs_to_many :assemblies end
上述关联需要在迁移中创建 assemblies_parts 表,而且该表无主键:
class CreateAssembliesPartsJoinTable < ActiveRecord::Migration[5.0]
def change
create_table :assemblies_parts, id: false do |t|
t.integer :assembly_id
t.integer :part_id
end
add_index :assemblies_parts, :assembly_id
add_index :assemblies_parts, :part_id
end
end
我们把 id: false 选项传给 create_table 方法,因为这个表不对应模型。只有这样,关联才能正常建立。如果在使用 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联时遇到奇怪的行为,例如提示模型 ID 损坏,或 ID 冲突,有可能就是因为创建了主键。
联结表还可以使用 create_join_table 方法创建:
class CreateAssembliesPartsJoinTable < ActiveRecord::Migration[5.0]
def change
create_join_table :assemblies, :parts do |t|
t.index :assembly_id
t.index :part_id
end
end
end
3.4 控制关联的作用域
默认情况下,关联只会查找当前模块作用域中的对象。如果在模块中定义 Active Record 模型,知道这一点很重要。例如:
module MyApplication
module Business
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord
has_one :account
end
class Account < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :supplier
end
end
end
上面的代码能正常运行,因为 Supplier 和 Account 在同一个作用域中。但下面这段代码就不行了,因为 Supplier 和 Account 在不同的作用域中:
module MyApplication
module Business
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord
has_one :account
end
end
module Billing
class Account < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :supplier
end
end
end
要想让处在不同命名空间中的模型正常建立关联,声明关联时要指定完整的类名:
module MyApplication
module Business
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord
has_one :account,
class_name: "MyApplication::Billing::Account"
end
end
module Billing
class Account < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :supplier,
class_name: "MyApplication::Business::Supplier"
end
end
end
3.5 双向关联
一般情况下,都要求能在关联的两端进行操作,即在两个模型中都要声明关联。
class Author < ApplicationRecord has_many :books end class Book < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :author end
通过关联的名称,Active Record 能探知这两个模型之间建立的是双向关联。这样一来,Active Record 只会加载一个 Author 对象副本,从而确保应用运行效率更高效,并避免数据不一致。
a = Author.first b = a.books.first a.first_name == b.author.first_name # => true a.first_name = 'David' a.first_name == b.author.first_name # => true
Active Record 能自动识别多数具有标准名称的双向关联。然而,具有下述选项的关联无法识别:
-
:conditions -
:through -
:polymorphic -
:class_name -
:foreign_key
例如,对下属模型来说:
class Author < ApplicationRecord has_many :books end class Book < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :writer, class_name: 'Author', foreign_key: 'author_id' end
Active Record 就无法自动识别这个双向关联:
a = Author.first b = a.books.first a.first_name == b.writer.first_name # => true a.first_name = 'David' a.first_name == b.writer.first_name # => false
Active Record 提供了 :inverse_of 选项,可以通过它明确声明双向关联:
class Author < ApplicationRecord has_many :books, inverse_of: 'writer' end class Book < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :writer, class_name: 'Author', foreign_key: 'author_id' end
在 has_many 声明中指定 :inverse_of 选项后,Active Record 便能识别双向关联:
a = Author.first b = a.books.first a.first_name == b.writer.first_name # => true a.first_name = 'David' a.first_name == b.writer.first_name # => true
inverse_of 有些限制:
- 不支持
:through关联; - 不支持
:polymorphic关联; - 不支持
:as选项;
4 关联详解
下面几小节详细说明各种关联,包括添加的方法和声明关联时可以使用的选项。
4.1 belongs_to 关联详解
belongs_to 关联创建一个模型与另一个模型之间的一对一关系。用数据库术语来说,就是这个类中包含外键。如果外键在另一个类中,应该使用 has_one 关联。
4.1.1 belongs_to 关联添加的方法
声明 belongs_to 关联后,所在的类自动获得了五个和关联相关的方法:
-
association -
association=(associate) -
build_association(attributes = {}) -
create_association(attributes = {}) -
create_association!(attributes = {})
这五个方法中的 association 要替换成传给 belongs_to 方法的第一个参数。对下述声明来说:
class Book < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :author end
Book 模型的每个实例都获得了这些方法:
author author= build_author create_author create_author!
在 has_one 和 belongs_to 关联中,必须使用 build_* 方法构建关联对象。association.build 方法是在 has_many 和 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联中使用的。创建关联对象要使用 create_* 方法。
4.1.1.1 association
如果关联的对象存在,association 方法会返回关联的对象。如果找不到关联的对象,返回 nil。
@author = @book.author
如果关联的对象之前已经取回,会返回缓存版本。如果不想使用缓存版本(强制读取数据库)在父对象上调用 #reload 方法。
@author = @book.reload.author
4.1.1.2 association=(associate)
association= 方法用于赋值关联的对象。这个方法的底层操作是,从关联对象上读取主键,然后把值赋给该主键对应的对象。
@book.author = @author
4.1.1.3 build_association(attributes = {})
build_association 方法返回该关联类型的一个新对象。这个对象使用传入的属性初始化,对象的外键会自动设置,但关联对象不会存入数据库。
@author = @book.build_author(author_number: 123,
author_name: "John Doe")
4.1.1.4 create_association(attributes = {})
create_association 方法返回该关联类型的一个新对象。这个对象使用传入的属性初始化,对象的外键会自动设置,只要能通过所有数据验证,就会把关联对象存入数据库。
@author = @book.create_author(author_number: 123,
author_name: "John Doe")
4.1.1.5 create_association!(attributes = {})
与 create_association 方法作用相同,但是如果记录无效,会抛出 ActiveRecord::RecordInvalid 异常。
4.1.2 belongs_to 方法的选项
Rails 的默认设置足够智能,能满足多数需求。但有时还是需要定制 belongs_to 关联的行为。定制的方法很简单,声明关联时传入选项或者使用代码块即可。例如,下面的关联使用了两个选项:
class Book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :author, dependent: :destroy,
counter_cache: true
end
belongs_to 关联支持下列选项:
-
:autosave -
:class_name -
:counter_cache -
:dependent -
:foreign_key -
:primary_key -
:inverse_of -
:polymorphic -
:touch -
:validate -
:optional
4.1.2.1 :autosave
如果把 :autosave 选项设为 true,保存父对象时,会自动保存所有子对象,并把标记为析构的子对象销毁。
4.1.2.2 :class_name
如果另一个模型无法从关联的名称获取,可以使用 :class_name 选项指定模型名。例如,如果一本书属于一位作者,但是表示作者的模型是 Patron,就可以这样声明关联:
class Book < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :author, class_name: "Patron" end
4.1.2.3 :counter_cache
:counter_cache 选项可以提高统计所属对象数量操作的效率。以下述模型为例:
class Book < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :author end class Author < ApplicationRecord has_many :books end
这样声明关联后,如果想知道 @author.books.size 的结果,要在数据库中执行 COUNT(*) 查询。如果不想执行这个查询,可以在声明 belongs_to 关联的模型中加入计数缓存功能:
class Book < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :author, counter_cache: true end class Author < ApplicationRecord has_many :books end
这样声明关联后,Rails 会及时更新缓存,调用 size 方法时会返回缓存中的值。
虽然 :counter_cache 选项在声明 belongs_to 关联的模型中设置,但实际使用的字段要添加到所关联的模型中(has_many 那一方)。针对上面的例子,要把 books_count 字段加入 Author 模型。
这个字段的名称也是可以设置的,把 counter_cache 选项的值换成列名即可。例如,不使用 books_count,而是使用 count_of_books:
class Book < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :author, counter_cache: :count_of_books end class Author < ApplicationRecord has_many :books end
只需在关联的 belongs_to 一侧指定 :counter_cache 选项。
计数缓存字段通过 attr_readonly 方法加入关联模型的只读属性列表中。
4.1.2.4 :dependent
:dependent 选项控制属主销毁后怎么处理关联的对象:
-
:destroy:也销毁关联的对象 -
:delete_all:直接从数据库中删除关联的对象(不执行回调) -
:nullify:把外键设为NULL(不执行回调) -
:restrict_with_exception:如果有关联的记录,抛出异常 -
:restrict_with_error:如果有关联的对象,为属主添加一个错误
在 belongs_to 关联和 has_many 关联配对时,不应该设置这个选项,否则会导致数据库中出现无主记录。
4.1.2.5 :foreign_key
按照约定,用来存储外键的字段名是关联名后加 _id。:foreign_key 选项可以设置要使用的外键名:
class Book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :author, class_name: "Patron",
foreign_key: "patron_id"
end
不管怎样,Rails 都不会自动创建外键字段,你要自己在迁移中创建。
4.1.2.6 :primary_key
按照约定,Rails 假定使用表中的 id 列保存主键。使用 :primary_key 选项可以指定使用其他列。
假如有个 users 表使用 guid 列存储主键,todos 想在 guid 列中存储用户的 ID,那么可以使用 primary_key 选项设置:
class User < ApplicationRecord self.primary_key = 'guid' # 主键是 guid,不是 id end class Todo < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :user, primary_key: 'guid' end
执行 @user.todos.create 时,@todo 记录的用户 ID 是 @user 的 guid 值。
4.1.2.7 :inverse_of
:inverse_of 选项指定 belongs_to 关联另一端的 has_many 和 has_one 关联名。不能和 :polymorphic 选项一起使用。
class Author < ApplicationRecord has_many :books, inverse_of: :author end class Book < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :author, inverse_of: :books end
4.1.2.8 :polymorphic
:polymorphic 选项为 true 时,表明这是个多态关联。多态关联已经详细介绍过多态关联。
4.1.2.9 :touch
如果把 :touch 选项设为 true,保存或销毁对象时,关联对象的 updated_at 或 updated_on 字段会自动设为当前时间。
class Book < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :author, touch: true end class Author < ApplicationRecord has_many :books end
在这个例子中,保存或销毁一本书后,会更新关联的作者的时间戳。还可指定要更新哪个时间戳字段:
class Book < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :author, touch: :books_updated_at end
4.1.2.10 :validate
如果把 :validate 选项设为 true,保存对象时,会同时验证关联的对象。该选项的默认值是 false,保存对象时不验证关联的对象。
4.1.2.11 :optional
如果把 :optional 选项设为 true,不会验证关联的对象是否存在。该选项的默认值是 false。
4.1.3 belongs_to 的作用域
有时可能需要定制 belongs_to 关联使用的查询,定制的查询可在作用域代码块中指定。例如:
class Book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :author, -> { where active: true },
dependent: :destroy
end
在作用域代码块中可以使用任何一个标准的查询方法。下面分别介绍这几个:
-
where -
includes -
readonly -
select
4.1.3.1 where
where 方法指定关联对象必须满足的条件。
class book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :author, -> { where active: true }
end
4.1.3.2 includes
includes 方法指定使用关联时要及早加载的间接关联。例如,有如下的模型:
class LineItem < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :book end class Book < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :author has_many :line_items end class Author < ApplicationRecord has_many :books end
如果经常要直接从商品上获取作者对象(@line_item.book.author),就可以在关联中把作者从商品引入图书中:
class LineItem < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :book, -> { includes :author }
end
class Book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :author
has_many :line_items
end
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books
end
直接关联没必要使用 includes。如果 Book belongs_to :author,那么需要使用时会自动及早加载作者。
4.1.3.3 readonly
如果使用 readonly,通过关联获取的对象是只读的。
4.1.3.4 select
select 方法用于覆盖检索关联对象使用的 SQL SELECT 子句。默认情况下,Rails 检索所有字段。
如果在 belongs_to 关联中使用 select 方法,应该同时设置 :foreign_key 选项,确保返回的结果正确。
4.1.4 什么时候保存对象
把对象赋值给 belongs_to 关联不会自动保存对象,也不会保存关联的对象。
4.2 has_one 关联详解
has_one 关联建立两个模型之间的一对一关系。用数据库术语来说,这种关联的意思是外键在另一个类中。如果外键在这个类中,应该使用 belongs_to 关联。
4.2.1 has_one 关联添加的方法
声明 has_one 关联后,声明所在的类自动获得了五个关联相关的方法:
-
association -
association=(associate) -
build_association(attributes = {}) -
create_association(attributes = {}) -
create_association!(attributes = {})
这五个方法中的 association 要替换成传给 has_one 方法的第一个参数。对如下的声明来说:
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord has_one :account end
每个 Supplier 模型实例都获得了这些方法:
account account= build_account create_account create_account!
在 has_one 和 belongs_to 关联中,必须使用 build_* 方法构建关联对象。association.build 方法是在 has_many 和 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联中使用的。创建关联对象要使用 create_* 方法。
4.2.1.1 association
如果关联的对象存在,association 方法会返回关联的对象。如果找不到关联的对象,返回 nil。
@account = @supplier.account
如果关联的对象之前已经取回,会返回缓存版本。如果不想使用缓存版本,而是强制重新从数据库中读取,在父对象上调用 #reload 方法。
@account = @supplier.reload.account
4.2.1.2 association=(associate)
association= 方法用于赋值关联的对象。这个方法的底层操作是,从对象上读取主键,然后把关联的对象的外键设为那个值。
@supplier.account = @account
4.2.1.3 build_association(attributes = {})
build_association 方法返回该关联类型的一个新对象。这个对象使用传入的属性初始化,和对象链接的外键会自动设置,但关联对象不会存入数据库。
@account = @supplier.build_account(terms: "Net 30")
4.2.1.4 create_association(attributes = {})
create_association 方法返回该关联类型的一个新对象。这个对象使用传入的属性初始化,和对象链接的外键会自动设置,只要能通过所有数据验证,就会把关联对象存入数据库。
@account = @supplier.create_account(terms: "Net 30")
4.2.1.5 create_association!(attributes = {})
与 create_association 方法作用相同,但是如果记录无效,会抛出 ActiveRecord::RecordInvalid 异常。
4.2.2 has_one 方法的选项
Rails 的默认设置足够智能,能满足多数需求。但有时还是需要定制 has_one 关联的行为。定制的方法很简单,声明关联时传入选项即可。例如,下面的关联使用了两个选项:
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord has_one :account, class_name: "Billing", dependent: :nullify end
has_one 关联支持下列选项:
-
:as -
:autosave -
:class_name -
:dependent -
:foreign_key -
:inverse_of -
:primary_key -
:source -
:source_type -
:through -
:validate
4.2.2.1 :as
:as 选项表明这是多态关联。前文已经详细介绍过多态关联。
4.2.2.2 :autosave
如果把 :autosave 选项设为 true,保存父对象时,会自动保存所有子对象,并把标记为析构的子对象销毁。
4.2.2.3 :class_name
如果另一个模型无法从关联的名称获取,可以使用 :class_name 选项指定模型名。例如,供应商有一个账户,但表示账户的模型是 Billing,那么就可以这样声明关联:
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord has_one :account, class_name: "Billing" end
4.2.2.4 :dependent
控制属主销毁后怎么处理关联的对象:
-
:destroy:也销毁关联的对象; -
:delete:直接把关联的对象从数据库中删除(不执行回调); -
:nullify:把外键设为NULL,不执行回调; -
:restrict_with_exception:有关联的对象时抛出异常; -
:restrict_with_error:有关联的对象时,向属主添加一个错误;
如果在数据库层设置了 NOT NULL 约束,就不能使用 :nullify 选项。如果 :dependent 选项没有销毁关联,就无法修改关联的对象,因为关联的对象的外键设置为不接受 NULL。
4.2.2.5 :foreign_key
按照约定,在另一个模型中用来存储外键的字段名是模型名后加 _id。:foreign_key 选项用于设置要使用的外键名:
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord has_one :account, foreign_key: "supp_id" end
不管怎样,Rails 都不会自动创建外键字段,你要自己在迁移中创建。
4.2.2.6 :inverse_of
:inverse_of 选项指定 has_one 关联另一端的 belongs_to 关联名。不能和 :through 或 :as 选项一起使用。
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord has_one :account, inverse_of: :supplier end class Account < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :supplier, inverse_of: :account end
4.2.2.7 :primary_key
按照约定,用来存储该模型主键的字段名 id。:primary_key 选项用于设置要使用的主键名。
4.2.2.8 :source
:source 选项指定 has_one :through 关联的源关联名称。
4.2.2.9 :source_type
:source_type 选项指定通过多态关联处理 has_one :through 关联的源关联类型。
4.2.2.10 :through
:through 选项指定用于执行查询的联结模型。前文详细介绍过 has_one :through 关联。
4.2.2.11 :validate
如果把 :validate 选项设为 true,保存对象时,会同时验证关联的对象。该选项的默认值是 false,即保存对象时不验证关联的对象。
4.2.3 has_one 的作用域
有时可能需要定制 has_one 关联使用的查询。定制的查询在作用域代码块中指定。例如:
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord
has_one :account, -> { where active: true }
end
在作用域代码块中可以使用任何一个标准的查询方法。下面介绍其中几个:
-
where -
includes -
readonly -
select
4.2.3.1 where
where 方法指定关联的对象必须满足的条件。
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord
has_one :account, -> { where "confirmed = 1" }
end
4.2.3.2 includes
includes 方法指定使用关联时要及早加载的间接关联。例如,有如下的模型:
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord has_one :account end class Account < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :supplier belongs_to :representative end class Representative < ApplicationRecord has_many :accounts end
如果经常直接获取供应商代表(@supplier.account.representative),可以把代表引入供应商和账户的关联中:
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord
has_one :account, -> { includes :representative }
end
class Account < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :supplier
belongs_to :representative
end
class Representative < ApplicationRecord
has_many :accounts
end
4.2.3.3 readonly
如果使用 readonly,通过关联获取的对象是只读的。
4.2.3.4 select
select 方法会覆盖获取关联对象使用的 SQL SELECT 子句。默认情况下,Rails 检索所有列。
4.2.4 检查关联的对象是否存在
检查关联的对象是否存在可以使用 association.nil? 方法:
if @supplier.account.nil? @msg = "No account found for this supplier" end
4.2.5 什么时候保存对象
把对象赋值给 has_one 关联时,那个对象会自动保存(因为要更新外键)。而且所有被替换的对象也会自动保存,因为外键也变了。
如果由于无法通过验证而导致上述保存失败,赋值语句返回 false,赋值操作会取消。
如果父对象(has_one 关联声明所在的模型)没保存(new_record? 方法返回 true),那么子对象也不会保存。只有保存了父对象,才会保存子对象。
如果赋值给 has_one 关联时不想保存对象,使用 association.build 方法。
4.3 has_many 关联详解
has_many 关联建立两个模型之间的一对多关系。用数据库术语来说,这种关联的意思是外键在另一个类中,指向这个类的实例。
4.3.1 has_many 关联添加的方法
声明 has_many 关联后,声明所在的类自动获得了 16 个关联相关的方法:
-
collection -
collection<<(object, …​) -
collection.delete(object, …​) -
collection.destroy(object, …​) -
collection=(objects) -
collection_singular_ids -
collection_singular_ids=(ids) -
collection.clear -
collection.empty? -
collection.size -
collection.find(…​) -
collection.where(…​) -
collection.exists?(…​) -
collection.build(attributes = {}, …​) -
collection.create(attributes = {}) -
collection.create!(attributes = {})
这些个方法中的 collection 要替换成传给 has_many 方法的第一个参数。collection_singular 要替换成第一个参数的单数形式。对如下的声明来说:
class Author < ApplicationRecord has_many :books end
每个 Author 模型实例都获得了这些方法:
books
books<<(object, ...)
books.delete(object, ...)
books.destroy(object, ...)
books=(objects)
book_ids
book_ids=(ids)
books.clear
books.empty?
books.size
books.find(...)
books.where(...)
books.exists?(...)
books.build(attributes = {}, ...)
books.create(attributes = {})
books.create!(attributes = {})
4.3.1.1 collection
collection 方法返回一个数组,包含所有关联的对象。如果没有关联的对象,则返回空数组。
@books = @author.books
4.3.1.2 collection<<(object, …​)
collection<< 方法向关联对象数组中添加一个或多个对象,并把各个所加对象的外键设为调用此方法的模型的主键。
@author.books << @book1
4.3.1.3 collection.delete(object, …​)
collection.delete 方法从关联对象数组中删除一个或多个对象,并把删除的对象外键设为 NULL。
@author.books.delete(@book1)
如果关联设置了 dependent: :destroy,还会销毁关联的对象;如果关联设置了 dependent: :delete_all,还会删除关联的对象。
4.3.1.4 collection.destroy(object, …​)
collection.destroy 方法在关联对象上调用 destroy 方法,从关联对象数组中删除一个或多个对象。
@author.books.destroy(@book1)
对象始终会从数据库中删除,忽略 :dependent 选项。
4.3.1.5 collection=(objects)
collection= 方法让关联对象数组只包含指定的对象,根据需求会添加或删除对象。改动会持久存入数据库。
4.3.1.6 collection_singular_ids
collection_singular_ids 方法返回一个数组,包含关联对象数组中各对象的 ID。
@book_ids = @author.book_ids
4.3.1.7 collection_singular_ids=(ids)
collection_singular_ids= 方法让关联对象数组中只包含指定的主键,根据需要会增删 ID。改动会持久存入数据库。
4.3.1.8 collection.clear
collection.clear 方法根据 dependent 选项指定的策略删除集合中的所有对象。如果没有指定这个选项,使用默认策略。has_many :through 关联的默认策略是 delete_all;has_many 关联的默认策略是,把外键设为 NULL。
@author.books.clear
如果设为 dependent: :destroy,对象会被删除,这与 dependent: :delete_all 一样。
4.3.1.9 collection.empty?
如果集合中没有关联的对象,collection.empty? 方法返回 true。
<% if @author.books.empty? %> No Books Found <% end %>
4.3.1.10 collection.size
collection.size 返回集合中的对象数量。
@book_count = @author.books.size
4.3.1.11 collection.find(…​)
collection.find 方法在集合中查找对象,使用的句法和选项跟 ActiveRecord::Base.find 方法一样。
@available_books = @author.books.find(1)
4.3.2 collection.where(…​)
collection.where 方法根据指定的条件在集合中查找对象,但对象是惰性加载的,即访问对象时才会查询数据库。
@available_books = @author.books.where(available: true) # 尚未查询 @available_book = @available_books.first # 现在查询数据库
4.3.2.1 collection.exists?(…​)
collection.exists? 方法根据指定的条件检查集合中是否有符合条件的对象,使用的句法和选项跟 ActiveRecord::Base.exists? 方法一样。
4.3.2.2 collection.build(attributes = {}, …​)
collection.build 方法返回一个或多个此种关联类型的新对象。这些对象会使用传入的属性初始化,还会创建对应的外键,但不会保存关联的对象。
@book = @author.books.build(published_at: Time.now,
book_number: "A12345")
@books = @author.books.build([
{ published_at: Time.now, book_number: "A12346" },
{ published_at: Time.now, book_number: "A12347" }
])
4.3.2.3 collection.create(attributes = {})
collection.create 方法返回一个或多个此种关联类型的新对象。这些对象会使用传入的属性初始化,还会创建对应的外键,只要能通过所有数据验证,就会保存关联的对象。
@book = @author.books.create(published_at: Time.now,
book_number: "A12345")
@books = @author.books.create([
{ published_at: Time.now, book_number: "A12346" },
{ published_at: Time.now, book_number: "A12347" }
])
4.3.3 collection.create!(attributes = {})
作用与 collection.create 相同,但如果记录无效,会抛出 ActiveRecord::RecordInvalid 异常。
4.3.4 has_many 方法的选项
Rails 的默认设置足够智能,能满足多数需求。但有时还是需要定制 has_many 关联的行为。定制的方法很简单,声明关联时传入选项即可。例如,下面的关联使用了两个选项:
class Author < ApplicationRecord has_many :books, dependent: :delete_all, validate: false end
has_many 关联支持以下选项:
-
:as -
:autosave -
:class_name -
:counter_cache -
:dependent -
:foreign_key -
:inverse_of -
:primary_key -
:source -
:source_type -
:through -
:validate
4.3.4.1 :as
:as 选项表明这是多态关联。前文已经详细介绍过多态关联。
4.3.4.2 :autosave
如果把 :autosave 选项设为 true,保存父对象时,会自动保存所有子对象,并把标记为析构的子对象销毁。
4.3.4.3 :class_name
如果另一个模型无法从关联的名称获取,可以使用 :class_name 选项指定模型名。例如,一位作者有多本图书,但表示图书的模型是 Transaction,那么可以这样声明关联:
class Author < ApplicationRecord has_many :books, class_name: "Transaction" end
4.3.4.4 :counter_cache
这个选项用于定制计数缓存列的名称。仅当定制了 belongs_to 关联的 :counter_cache 选项时才需要设定这个选项。
4.3.4.5 :dependent
设置销毁属主时怎么处理关联的对象:
-
:destroy:也销毁所有关联的对象; -
:delete_all:直接把所有关联的对象从数据库中删除(不执行回调); -
:nullify:把外键设为NULL,不执行回调; -
:restrict_with_exception:有关联的对象时抛出异常; -
:restrict_with_error:有关联的对象时,向属主添加一个错误;
4.3.4.6 :foreign_key
按照约定,另一个模型中用来存储外键的字段名是模型名后加 _id。:foreign_key 选项用于设置要使用的外键名:
class Author < ApplicationRecord has_many :books, foreign_key: "cust_id" end
不管怎样,Rails 都不会自动创建外键字段,你要自己在迁移中创建。
4.3.4.7 :inverse_of
:inverse_of 选项指定 has_many 关联另一端的 belongs_to 关联名。不能和 :through 或 :as 选项一起使用。
class Author < ApplicationRecord has_many :books, inverse_of: :author end class Book < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :author, inverse_of: :books end
4.3.4.8 :primary_key
按照约定,用来存储该模型主键的字段名为 id。:primary_key 选项用于设置要使用的主键名。
假设 users 表的主键是 id,但还有一个 guid 列。根据要求,todos 表中应该使用 guid 列作为外键,而不是 id 列。这种需求可以这么实现:
class User < ApplicationRecord has_many :todos, primary_key: :guid end
如果执行 @todo = @user.todos.create 创建新的待办事项,那么 @todo.user_id 就是 @user 记录中 guid 字段的值。
4.3.4.9 :source
:source 选项指定 has_many :through 关联的源关联名称。只有无法从关联名中解出源关联的名称时才需要设置这个选项。
4.3.4.10 :source_type
:source_type 选项指定通过多态关联处理 has_many :through 关联的源关联类型。
4.3.4.11 :through
:through 选项指定一个联结模型,查询通过它执行。前文说过,has_many :through 关联是实现多对多关联的方式之一。
4.3.4.12 :validate
如果把 :validate 选项设为 false,保存对象时,不验证关联的对象。该选项的默认值是 true,即保存对象时验证关联的对象。
4.3.5 has_many 的作用域
有时可能需要定制 has_many 关联使用的查询。定制的查询在作用域代码块中指定。例如:
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books, -> { where processed: true }
end
在作用域代码块中可以使用任何一个标准的查询方法。下面介绍其中几个:
-
where -
extending -
group -
includes -
limit -
offset -
order -
readonly -
select -
distinct
4.3.5.1 where
where 方法指定关联的对象必须满足的条件。
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :confirmed_books, -> { where "confirmed = 1" },
class_name: "Book"
end
条件还可以使用散列指定:
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :confirmed_books, -> { where confirmed: true },
class_name: "Book"
end
如果 where 使用散列形式,通过这个关联创建的记录会自动使用散列中的作用域。针对上面的例子,使用 @author.confirmed_books.create 或 @author.confirmed_books.build 创建图书时,会自动把 confirmed 列的值设为 true。
4.3.5.2 extending
extending 方法指定一个模块名,用于扩展关联代理。后文会详细介绍关联扩展。
4.3.5.3 group
group 方法指定一个属性名,用在 SQL GROUP BY 子句中,分组查询结果。
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :line_items, -> { group 'books.id' },
through: :books
end
4.3.5.4 includes
includes 方法指定使用关联时要及早加载的间接关联。例如,有如下的模型:
class Author < ApplicationRecord has_many :books end class Book < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :author has_many :line_items end class LineItem < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :book end
如果经常要直接获取作者购买的商品(@author.books.line_items),可以把商品引入作者和图书的关联中:
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books, -> { includes :line_items }
end
class Book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :author
has_many :line_items
end
class LineItem < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :book
end
4.3.5.5 limit
limit 方法限制通过关联获取的对象数量。
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :recent_books,
-> { order('published_at desc').limit(100) },
class_name: "Book",
end
4.3.5.6 offset
offset 方法指定通过关联获取对象时的偏移量。例如,-> { offset(11) } 会跳过前 11 个记录。
4.3.5.7 order
order 方法指定获取关联对象时使用的排序方式,用在 SQL ORDER BY 子句中。
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books, -> { order "date_confirmed DESC" }
end
4.3.5.8 readonly
如果使用 readonly,通过关联获取的对象是只读的。
4.3.5.9 select
select 方法用于覆盖检索关联对象数据的 SQL SELECT 子句。默认情况下,Rails 会检索所有列。
如果设置 select 选项,记得要包含主键和关联模型的外键。否则,Rails 会抛出异常。
4.3.5.10 distinct
使用 distinct 方法可以确保集合中没有重复的对象。与 :through 选项一起使用最有用。
class Person < ApplicationRecord has_many :readings has_many :articles, through: :readings end person = Person.create(name: 'John') article = Article.create(name: 'a1') person.articles << article person.articles << article person.articles.inspect # => [#<Article id: 5, name: "a1">, #<Article id: 5, name: "a1">] Reading.all.inspect # => [#<Reading id: 12, person_id: 5, article_id: 5>, #<Reading id: 13, person_id: 5, article_id: 5>]
在上面的代码中,读者读了两篇文章,即使是同一篇文章,person.articles 也会返回两个对象。
下面加入 distinct 方法:
class Person
has_many :readings
has_many :articles, -> { distinct }, through: :readings
end
person = Person.create(name: 'Honda')
article = Article.create(name: 'a1')
person.articles << article
person.articles << article
person.articles.inspect # => [#<Article id: 7, name: "a1">]
Reading.all.inspect # => [#<Reading id: 16, person_id: 7, article_id: 7>, #<Reading id: 17, person_id: 7, article_id: 7>]
在这段代码中,读者还是读了两篇文章,但 person.articles 只返回一个对象,因为加载的集合已经去除了重复元素。
如果要确保只把不重复的记录写入关联模型的数据表(这样就不会从数据库中获取重复记录了),需要在数据表上添加唯一性索引。例如,数据表名为 readings,我们要保证其中所有的文章都没重复,可以在迁移中加入以下代码:
add_index :readings, [:person_id, :article_id], unique: true
添加唯一性索引之后,尝试为同一个人添加两篇相同的文章会抛出 ActiveRecord::RecordNotUnique 异常:
person = Person.create(name: 'Honda') article = Article.create(name: 'a1') person.articles << article person.articles << article # => ActiveRecord::RecordNotUnique
注意,使用 include? 等方法检查唯一性可能导致条件竞争。不要使用 include? 确保关联的唯一性。还是以前面的文章模型为例,下面的代码会导致条件竞争,因为多个用户可能会同时执行这一操作:
person.articles << article unless person.articles.include?(article)
4.3.6 什么时候保存对象
把对象赋值给 has_many 关联时,会自动保存对象(因为要更新外键)。如果一次赋值多个对象,所有对象都会自动保存。
如果由于无法通过验证而导致保存失败,赋值语句返回 false,赋值操作会取消。
如果父对象(has_many 关联声明所在的模型)没保存(new_record? 方法返回 true),那么子对象也不会保存。只有保存了父对象,才会保存子对象。
如果赋值给 has_many 关联时不想保存对象,使用 collection.build 方法。
4.4 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联详解
has_and_belongs_to_many 关联建立两个模型之间的多对多关系。用数据库术语来说,这种关联的意思是有个联结表包含指向这两个类的外键。
4.4.1 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联添加的方法
声明 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联后,声明所在的类自动获得了 16 个关联相关的方法:
-
collection -
collection<<(object, …​) -
collection.delete(object, …​) -
collection.destroy(object, …​) -
collection=(objects) -
collection_singular_ids -
collection_singular_ids=(ids) -
collection.clear -
collection.empty? -
collection.size -
collection.find(…​) -
collection.where(…​) -
collection.exists?(…​) -
collection.build(attributes = {}) -
collection.create(attributes = {}) -
collection.create!(attributes = {})
这些个方法中的 collection 要替换成传给 has_and_belongs_to_many 方法的第一个参数。collection_singular 要替换成第一个参数的单数形式。对如下的声明来说:
class Part < ApplicationRecord has_and_belongs_to_many :assemblies end
每个 Part 模型实例都获得了这些方法:
assemblies
assemblies<<(object, ...)
assemblies.delete(object, ...)
assemblies.destroy(object, ...)
assemblies=(objects)
assembly_ids
assembly_ids=(ids)
assemblies.clear
assemblies.empty?
assemblies.size
assemblies.find(...)
assemblies.where(...)
assemblies.exists?(...)
assemblies.build(attributes = {}, ...)
assemblies.create(attributes = {})
assemblies.create!(attributes = {})
4.4.1.1 额外的列方法
如果 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联使用的联结表中,除了两个外键之外还有其他列,通过关联获取的记录中会包含这些列,但是只读的,因为 Rails 不知道如何保存对这些列的改动。
在 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联的联结表中使用其他字段的功能已经废弃。如果在多对多关联中需要使用这么复杂的数据表,应该用 has_many :through 关联代替 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联。
4.4.1.2 collection
collection 方法返回一个数组,包含所有关联的对象。如果没有关联的对象,则返回空数组。
@assemblies = @part.assemblies
4.4.1.3 collection<<(object, …​)
collection<< 方法向集合中添加一个或多个对象,并在联结表中创建相应的记录。
@part.assemblies << @assembly1
这个方法是 collection.concat 和 collection.push 的别名。
4.4.1.4 collection.delete(object, …​)
collection.delete 方法从集合中删除一个或多个对象,并删除联结表中相应的记录,但是不会销毁对象。
@part.assemblies.delete(@assembly1)
4.4.1.5 collection.destroy(object, …​)
collection.destroy 方法把集合中指定对象在联结表中的记录删除。这个方法不会销毁对象本身。
@part.assemblies.destroy(@assembly1)
4.4.1.6 collection=(objects)
collection= 方法让集合只包含指定的对象,根据需求会添加或删除对象。改动会持久存入数据库。
4.4.1.7 collection_singular_ids
collection_singular_ids 方法返回一个数组,包含集合中各对象的 ID。
@assembly_ids = @part.assembly_ids
4.4.1.8 collection_singular_ids=(ids)
collection_singular_ids= 方法让集合中只包含指定的主键,根据需要会增删 ID。改动会持久存入数据库。
4.4.1.9 collection.clear
collection.clear 方法删除集合中的所有对象,并把联结表中的相应记录删除。这个方法不会销毁关联的对象。
4.4.1.10 collection.empty?
如果集合中没有任何关联的对象,collection.empty? 方法返回 true。
<% if @part.assemblies.empty? %> This part is not used in any assemblies <% end %>
4.4.1.11 collection.size
collection.size 方法返回集合中的对象数量。
@assembly_count = @part.assemblies.size
4.4.1.12 collection.find(…​)
collection.find 方法在集合中查找对象,使用的句法和选项跟 ActiveRecord::Base.find 方法一样。此外还限制对象必须在集合中。
@assembly = @part.assemblies.find(1)
4.4.1.13 collection.where(…​)
collection.where 方法根据指定的条件在集合中查找对象,但对象是惰性加载的,访问对象时才执行查询。此外还限制对象必须在集合中。
@new_assemblies = @part.assemblies.where("created_at > ?", 2.days.ago)
4.4.1.14 collection.exists?(…​)
collection.exists? 方法根据指定的条件检查集合中是否有符合条件的对象,使用的句法和选项跟 ActiveRecord::Base.exists? 方法一样。
4.4.1.15 collection.build(attributes = {})
collection.build 方法返回一个此种关联类型的新对象。这个对象会使用传入的属性初始化,还会在联结表中创建对应的记录,但不会保存关联的对象。
@assembly = @part.assemblies.build({assembly_name: "Transmission housing"})
4.4.1.16 collection.create(attributes = {})
collection.create 方法返回一个此种关联类型的新对象。这个对象会使用传入的属性初始化,还会在联结表中创建对应的记录,只要能通过所有数据验证,就保存关联对象。
@assembly = @part.assemblies.create({assembly_name: "Transmission housing"})
4.4.1.17 collection.create!(attributes = {})
作用和 collection.create 相同,但如果记录无效,会抛出 ActiveRecord::RecordInvalid 异常。
4.4.2 has_and_belongs_to_many 方法的选项
Rails 的默认设置足够智能,能满足多数需求。但有时还是需要定制 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联的行为。定制的方法很简单,声明关联时传入选项即可。例如,下面的关联使用了两个选项:
class Parts < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :assemblies, -> { readonly },
autosave: true
end
has_and_belongs_to_many 关联支持以下选项:
-
:association_foreign_key -
:autosave -
:class_name -
:foreign_key -
:join_table -
:validate
4.4.2.1 :association_foreign_key
按照约定,在联结表中用来指向另一个模型的外键名是模型名后加 _id。:association_foreign_key 选项用于设置要使用的外键名:
:foreign_key 和 :association_foreign_key 这两个选项在设置多对多自联结时很有用。例如:
class User < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :friends,
class_name: "User",
foreign_key: "this_user_id",
association_foreign_key: "other_user_id"
end
4.4.2.2 :autosave
如果把 :autosave 选项设为 true,保存父对象时,会自动保存所有子对象,并把标记为析构的子对象销毁。
4.4.2.3 :class_name
如果另一个模型无法从关联的名称获取,可以使用 :class_name 选项指定。例如,一个部件由多个装配件组成,但表示装配件的模型是 Gadget,那么可以这样声明关联:
class Parts < ApplicationRecord has_and_belongs_to_many :assemblies, class_name: "Gadget" end
4.4.2.4 :foreign_key
按照约定,在联结表中用来指向模型的外键名是模型名后加 _id。:foreign_key 选项用于设置要使用的外键名:
class User < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :friends,
class_name: "User",
foreign_key: "this_user_id",
association_foreign_key: "other_user_id"
end
4.4.2.5 :join_table
如果默认按照字典顺序生成的联结表名不能满足要求,可以使用 :join_table 选项指定。
4.4.2.6 :validate
如果把 :validate 选项设为 false,保存对象时,不会验证关联的对象。该选项的默认值是 true,即保存对象时验证关联的对象。
4.4.3 has_and_belongs_to_many 的作用域
有时可能需要定制 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联使用的查询。定制的查询在作用域代码块中指定。例如:
class Parts < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :assemblies, -> { where active: true }
end
在作用域代码块中可以使用任何一个标准的查询方法。下面分别介绍其中几个:
-
where -
extending -
group -
includes -
limit -
offset -
order -
readonly -
select -
distinct
4.4.3.1 where
where 方法指定关联的对象必须满足的条件。
class Parts < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :assemblies,
-> { where "factory = 'Seattle'" }
end
条件还可以使用散列指定:
class Parts < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :assemblies,
-> { where factory: 'Seattle' }
end
如果 where 使用散列形式,通过这个关联创建的记录会自动使用散列中的作用域。针对上面的例子,使用 @parts.assemblies.create 或 @parts.assemblies.build 创建订单时,会自动把 factory 字段的值设为 "Seattle"。
4.4.3.2 extending
extending 方法指定一个模块名,用来扩展关联代理。后文会详细介绍关联扩展。
4.4.3.3 group
group 方法指定一个属性名,用在 SQL GROUP BY 子句中,分组查询结果。
class Parts < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :assemblies, -> { group "factory" }
end
4.4.3.4 includes
includes 方法指定使用关联时要及早加载的间接关联。
4.4.3.5 limit
limit 方法限制通过关联获取的对象数量。
class Parts < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :assemblies,
-> { order("created_at DESC").limit(50) }
end
4.4.3.6 offset
offset 方法指定通过关联获取对象时的偏移量。例如,-> { offset(11) } 会跳过前 11 个记录。
4.4.3.7 order
order 方法指定获取关联对象时使用的排序方式,用在 SQL ORDER BY 子句中。
class Parts < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :assemblies,
-> { order "assembly_name ASC" }
end
4.4.3.8 readonly
如果使用 readonly,通过关联获取的对象是只读的。
4.4.3.9 select
select 方法用于覆盖检索关联对象数据的 SQL SELECT 子句。默认情况下,Rails 检索所有列。
4.4.3.10 distinct
distinct 方法用于删除集合中重复的对象。
4.4.4 什么时候保存对象
把对象赋值给 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联时,会自动保存对象(因为要更新外键)。如果一次赋值多个对象,所有对象都会自动保存。
如果由于无法通过验证而导致保存失败,赋值语句返回 false,赋值操作会取消。
如果父对象(has_and_belongs_to_many 关联声明所在的模型)没保存(new_record? 方法返回 true),那么子对象也不会保存。只有保存了父对象,才会保存子对象。
如果赋值给 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联时不想保存对象,使用 collection.build 方法。
4.5 关联回调
普通回调会介入 Active Record 对象的生命周期,在多个时刻处理对象。例如,可以使用 :before_save 回调在保存对象之前处理对象。
关联回调和普通回调差不多,只不过由集合生命周期中的事件触发。关联回调有四种:
-
before_add -
after_add -
before_remove -
after_remove
关联回调在声明关联时定义。例如:
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books, before_add: :check_credit_limit
def check_credit_limit(book)
...
end
end
Rails 会把要添加或删除的对象传入回调。
同一事件可以触发多个回调,多个回调使用数组指定:
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books,
before_add: [:check_credit_limit, :calculate_shipping_charges]
def check_credit_limit(book)
...
end
def calculate_shipping_charges(book)
...
end
end
如果 before_add 回调抛出异常,不会把对象添加到集合中。类似地,如果 before_remove 抛出异常,对象不会从集合中删除。
4.6 关联扩展
Rails 基于关联代理对象自动创建的功能是死的,可以通过匿名模块、新的查找方法、创建对象的方法等进行扩展。例如:
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books do
def find_by_book_prefix(book_number)
find_by(category_id: book_number[0..2])
end
end
end
如果扩展要在多个关联中使用,可以将其写入具名扩展模块。例如:
module FindRecentExtension
def find_recent
where("created_at > ?", 5.days.ago)
end
end
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books, -> { extending FindRecentExtension }
end
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord
has_many :deliveries, -> { extending FindRecentExtension }
end
在扩展中可以使用如下 proxy_association 方法的三个属性获取关联代理的内部信息:
-
proxy_association.owner:返回关联所属的对象; -
proxy_association.reflection:返回描述关联的反射对象; -
proxy_association.target:返回belongs_to或has_one关联的关联对象,或者has_many或has_and_belongs_to_many关联的关联对象集合;
5 单表继承
有时可能想在不同的模型中共用相同的字段和行为。假如有 Car、Motorcycle 和 Bicycle 三个模型,我们想在它们中共用 color 和 price 字段,但是各自的具体行为不同,而且使用不同的控制器。
在 Rails 中实现这一需求非常简单。首先,生成基模型 Vehicle:
$ rails generate model vehicle type:string color:string price:decimal{10.2}
注意到了吗,我们添加了一个“type”字段?既然所有模型都保存在这一个数据库表中,Rails 会把保存的模型名存储在这一列中。对这个例子来说,“type”字段的值可能是“Car”、“Motorcycle”或“Bicycle”。如果表中没有“type”字段,单表继承无法工作。
然后,生成三个模型,都继承自 Vehicle。为此,可以使用 parent=PARENT 选项。这样,生成的模型继承指定的父模型,而且不生成对应的迁移(因为表已经存在)。
例如,生成 Car 模型的命令是:
$ rails generate model car --parent=Vehicle
生成的模型如下:
class Car < Vehicle end
这意味着,添加到 Vehicle 中的所有行为在 Car 中都可用,例如关联、公开方法,等等。
创建一辆汽车,相应的记录保存在 vehicles 表中,而且 type 字段的值是“Car”:
Car.create(color: 'Red', price: 10000)
对应的 SQL 如下:
INSERT INTO "vehicles" ("type", "color", "price") VALUES ('Car', 'Red', 10000)
查询汽车记录时只会搜索此类车辆:
Car.all
执行的查询如下:
SELECT "vehicles".* FROM "vehicles" WHERE "vehicles"."type" IN ('Car')
反馈
我们鼓励您帮助提高本指南的质量。
如果看到如何错字或错误,请反馈给我们。 您可以阅读我们的文档贡献指南。
您还可能会发现内容不完整或不是最新版本。 请添加缺失文档到 master 分支。请先确认 Edge Guides 是否已经修复。 关于用语约定,请查看Ruby on Rails 指南指导。
无论什么原因,如果你发现了问题但无法修补它,请创建 issue。
最后,欢迎到 rubyonrails-docs 邮件列表参与任何有关 Ruby on Rails 文档的讨论。